What Materials Are Used to Make a 3D Printed House?
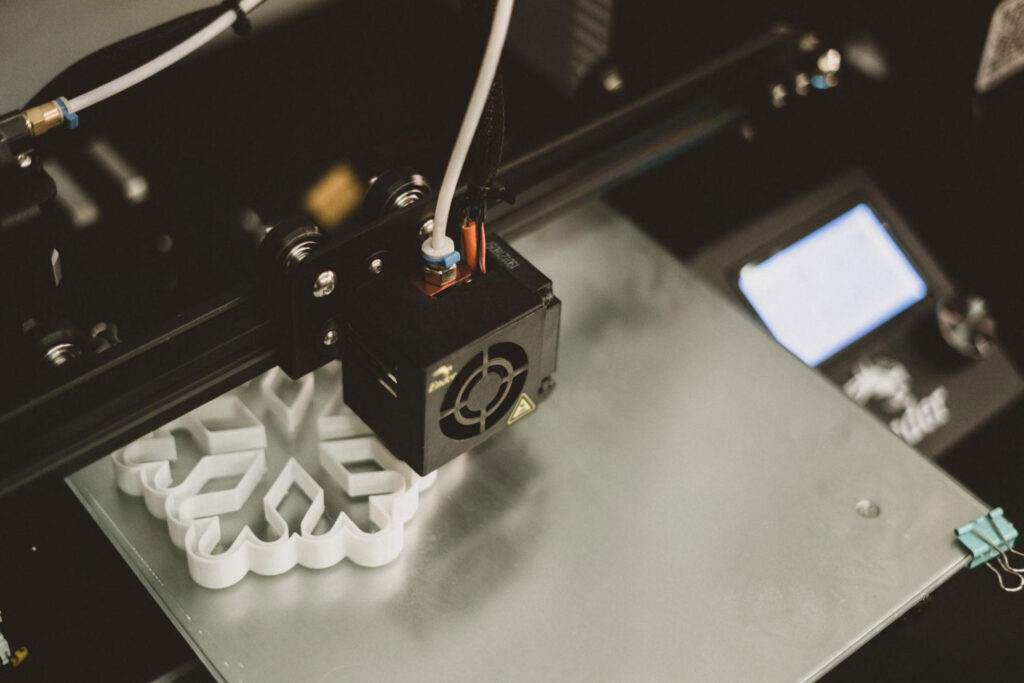
Technology inevitably evolves throughout the years and continues to impart not only valuable information but also advancements that provide us with so much ease — and one of those is 3D printing. Using a 3D printer, you can make all sorts of fun, interesting, and useful projects such as toys, tools, desk and cable organizers, pen holders, furniture, and more. It’s also been introduced and is highly useful to different industries such as education, aerospace, manufacturing, robotics, and construction.
Now in terms of construction, 3D printing is revolutionizing this industry through the creation of 3D printed houses. A 3D printed house is basically a house that’s built using the 3D printing technology method — which is a faster method compared to the traditional construction process. It may be seen as unconventional at first since it’s unlike the conventional way of building houses, but 3D printed houses are actually safe and durable and can withstand different harsh weather conditions, temperature changes, and natural disasters such as typhoons and earthquakes. Just like traditionally constructed houses, 3D printed houses are also built with materials that are commonly used in a regular construction process. With that said, let’s have a look at the materials used to make a 3D-printed house.
Recycled Plastic
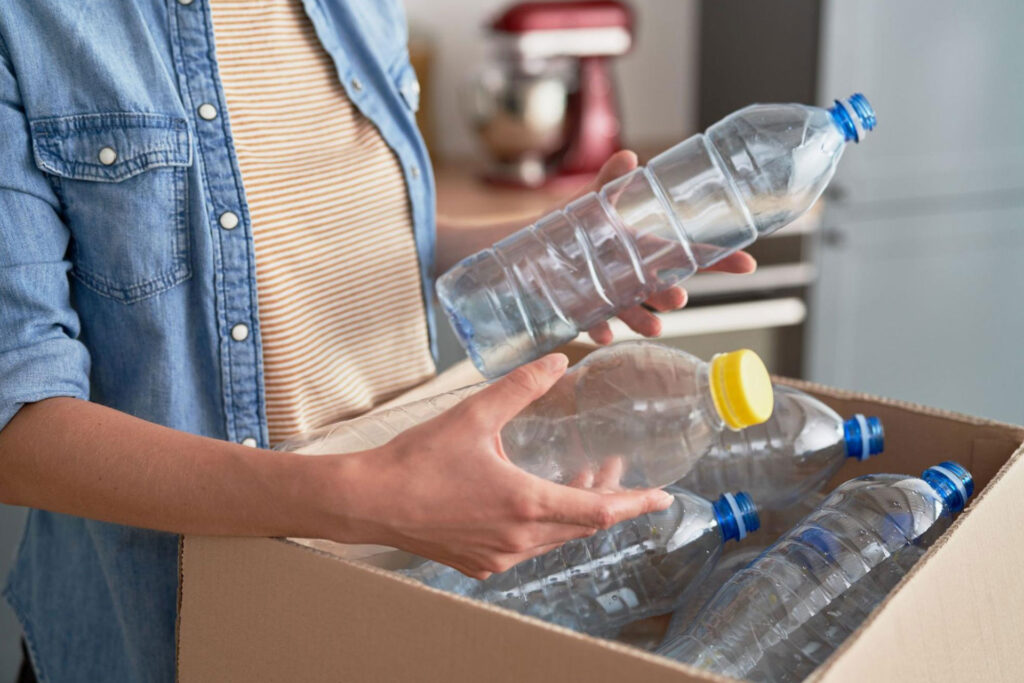

Yes, even recycled plastic can be used in 3D print houses. Since 3D printed houses have become more common these days, especially with the use of different technological advancements, engineers are now also looking into more innovative ways to elevate the construction industry and revolutionize the way structures are built.
Azure Printed Homes, a construction company based in Los Angeles, California, made use of recycled plastic to 3D print houses. With their vision to build homes that are sustainable and at the same time affordable, Azure was able to come up with a way to build homes in an environmentally friendly way — recycled plastic, which helped in reducing the amount of waste in landfills. Instead of using concrete, they aimed at recycling plastic to build homes. They were also able to come up with an estimate that 3D printed houses are cheaper than conventionally built homes by at least 20 to 30 percent. And with the use of 3D printers, the construction process can be accomplished faster.
Geopolymers
3D printing technology allows for a wide range of innovations using different specialized materials, creating the most intricate designs. And one of these materials is geopolymers, which are a set of inorganic polymeric and shapeless materials used to build 3D printed houses. One of the most notable advantages of using geopolymer is that it is low cost, eco-friendly, and is able to utilize solid wastes while still having low environmental load and energy consumption.
Concrete
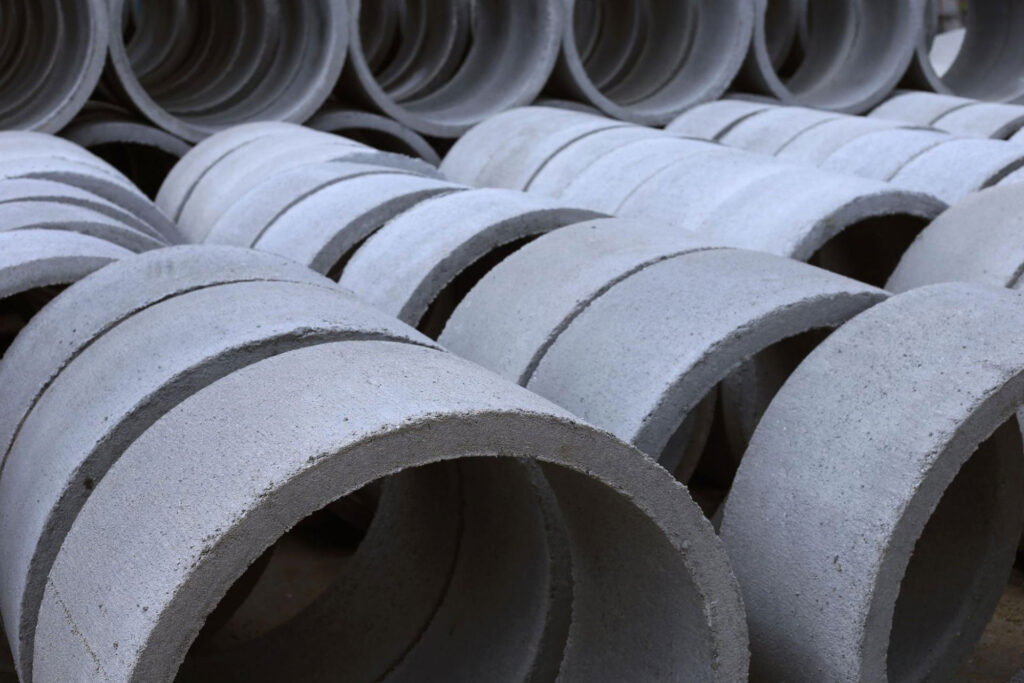

Concrete is one of the most popularly used materials in 3D printing construction, mainly due to its high strength, which is a necessity when you’re building houses and other structures. In 3D printing construction, 3D printed concrete is typically mixed with additives such as fibers, geopolymers, superplasticizers, and other materials, preparing the concrete for the 3D printing process.
Mortar
Mortar is used to bind bricks and stone together in masonry construction, helping to seal the gaps and even out the weight. Most commonly, in traditional construction, mortars are used as binders, but in 3D printing, it is being utilized to construct 3D printed houses. This is because mortars are essentially easier to work with compared to concrete, which means there’s also lesser damage to the environment. However, in terms of strength, concrete is still winning.
Soil
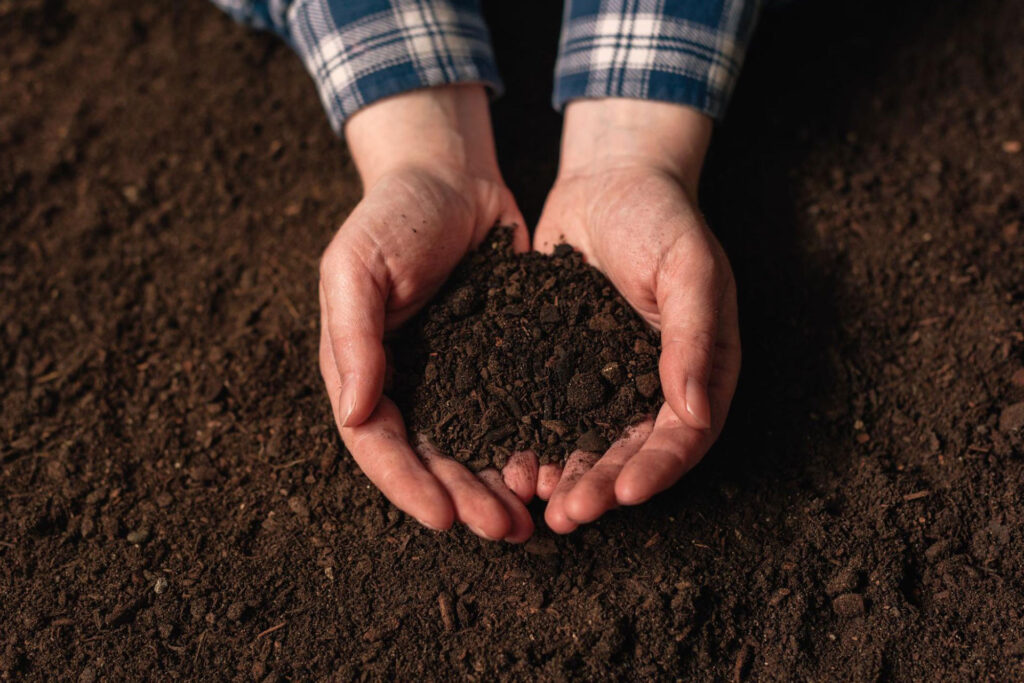

Soil is much more than just something we use for planting or a surface we walk on because it can also be used to build 3D printed houses. In fact, the soil is seen as an environmentally friendly and cost and time-efficient material to work with. It was WASP and MCA (Mario Cucinella Architects) who embarked on building 3D printed houses that are sustainable using “earth found on the spot” along with the combination of old material and state-of-the-art technology. Through their vision, they were able to 3D print the “Gaia,” an eco-friendly house. The Gaia was actually the first 3D printed mud house that was made using soil and other natural materials such as lime and rice husks. Using soil to build 3D printed houses came off as a smart and practical move to save the environment and at the same time provide a solution to the lack of affordable housing.
Clay
Clay is another local raw earth material that can be used by 3D print houses. TECLA or Technology and Clay was a product of project research done by Mario Cucinella and the founder of WASP, Massimo Moretti — which was centered around seeking ways to provide sustainable homes through the use of raw materials found on the spot. Hence, the creation of the TECLA house, a 3D printed house made out of clay. It was also the first 3D printed structure made from a mixture of local raw earth materials and water.
Sand
It may not seem like sand can be used to build a sturdy house or structure, but it is a substantial material that’s seen as a viable material for 3D printing construction. With the help of 3D printing technologies such as binder jetting and powder-bed process, it makes the sand stronger compared to reinforced concrete. Using sand to build 3D printed houses is inexpensive and the printing process itself is fairly cheap and quick as well, which in turn is able to provide both temporary and permanent affordable housing.
In need of someone to help you build your own 3D printed house? Contact us today, so we can answer all your inquiries!














