3D Printing vs. Traditional Manufacturing: What’s Their Difference?
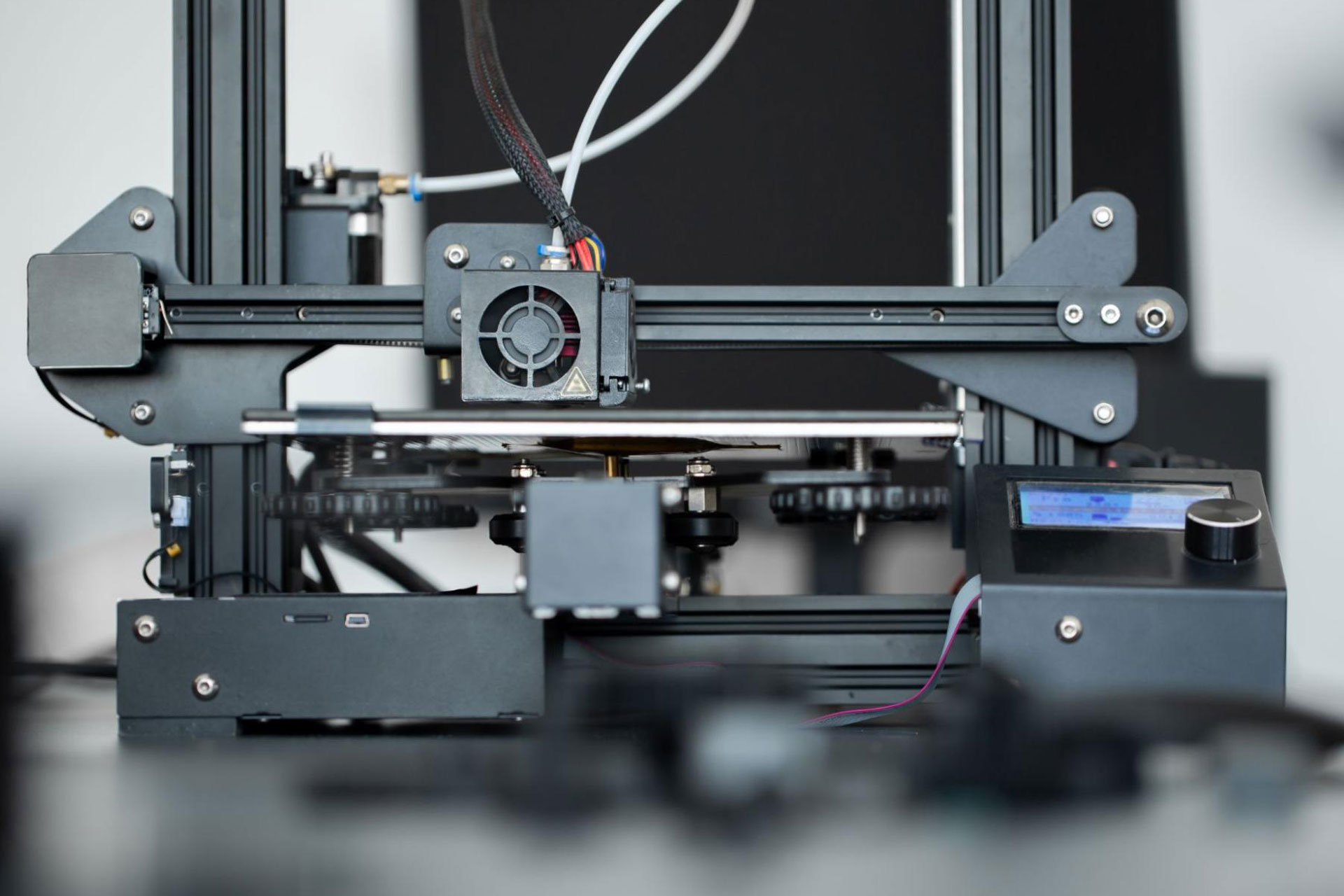
In today’s time, different technology advancements are being made and are providing ease and convenience to many businesses, especially manufacturing businesses. The process of manufacturing varies depending on the kind of product being produced and how many of them are needed. It also requires human labor, functional machinery or equipment, and others. However, with the high competition in the market today, businesses are also starting to elevate their way of manufacturing to cope with demands and produce more efficient products at a reasonable time.
When it comes to the process of manufacturing, traditional manufacturing comes to mind often. Although considering the advancements in technology, 3D printing is also making a name for itself in many businesses of varying industries.
What is 3D Printing?

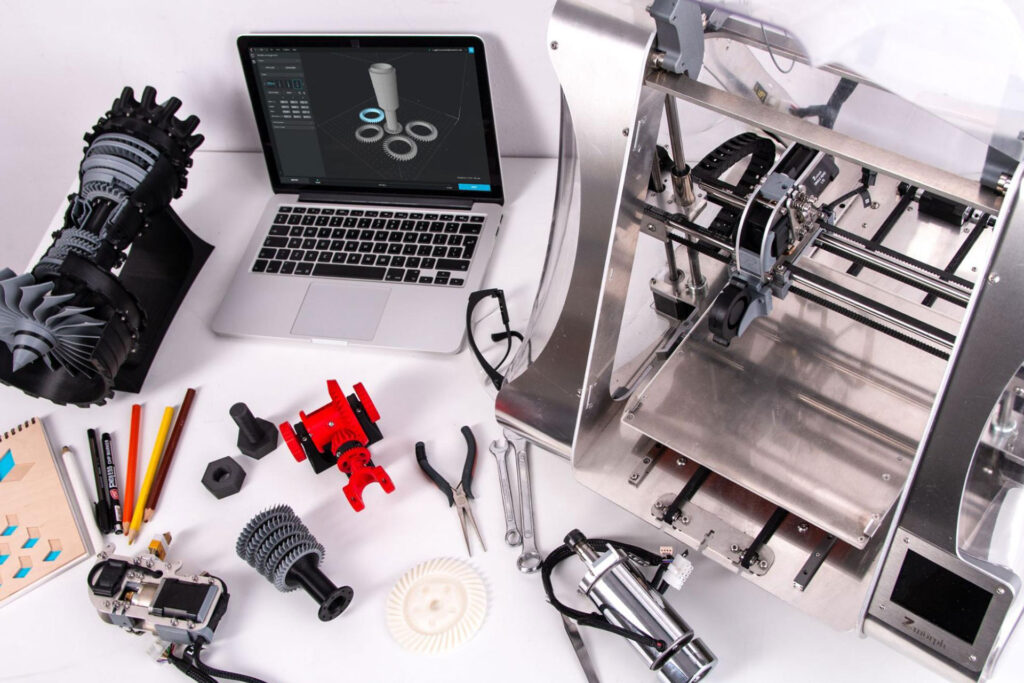
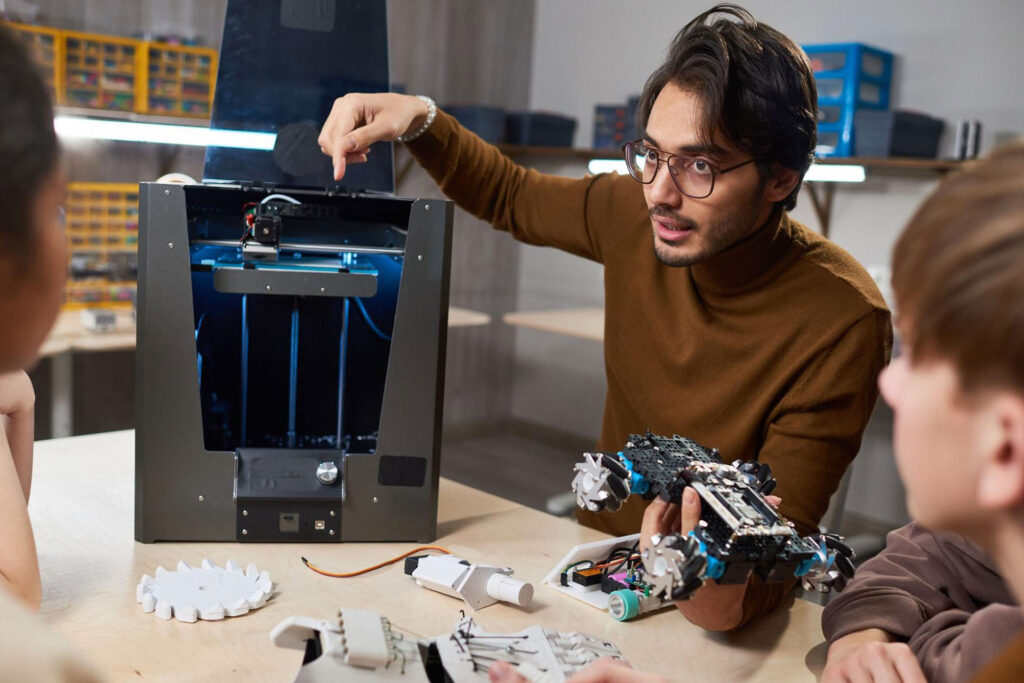
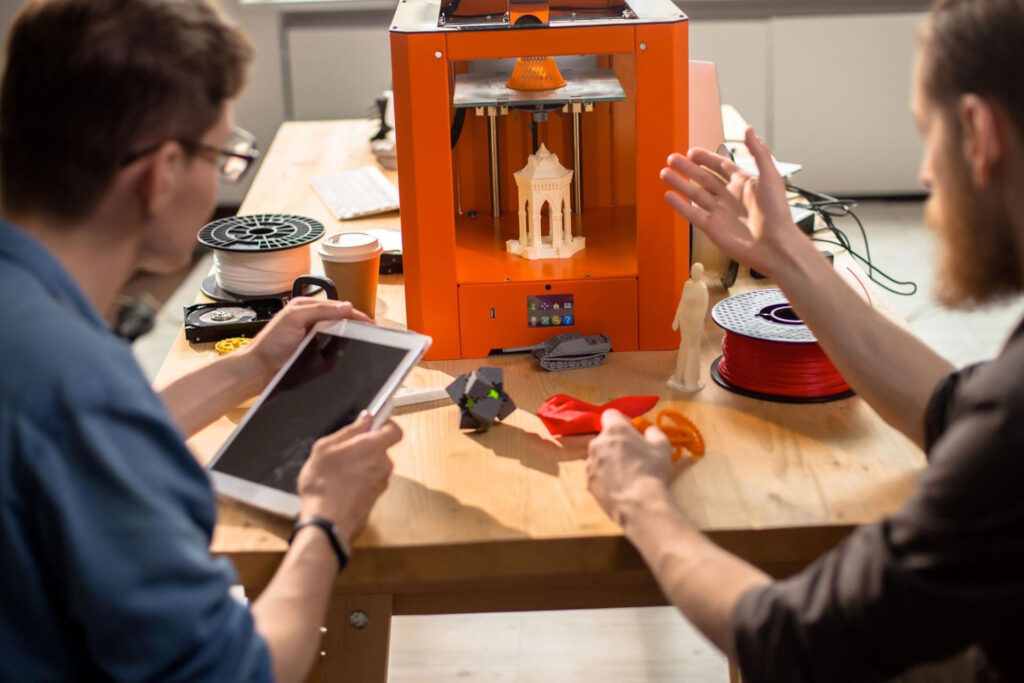
With the advanced features of 3D printing, you would think that it was a newly built technology, but it’s actually been around for quite some time already. In its earlier years, however, it wasn’t as high-performing as it is now and didn’t have many material properties. 3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process that creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer through a digital design. It also has made some remarkable benefits that industries such as education, automotive, aerospace, and more have been reaping, changing, and improving their production in the long run. Metal, plastic, carbon fiber, and powders are just some of the materials used for 3D printing.
What is Traditional Manufacturing?

Traditional manufacturing is a method of production that focuses on a specific number of products for every period of production while still holding a reserve for unexpected demands and shortages. Some industries that are known for making use of traditional manufacturing are furniture, clothing, textiles, and toys.
Now that you’ve gone through the gist of what 3D printing and traditional manufacturing are, how do you think they differ from each other? Let’s look at some factors that can further show their differences:
Scope and Complexity of Designs
One of the distinct functions of 3D printing is that it can produce parts even with the most complex designs, which can be impossible or too difficult for traditional manufacturing to do. Usually, with traditional manufacturing, producing parts with complex designs would entail higher costs. But with additive manufacturing, costs will not be affected by how complex the design is and the process will still remain the same.
Material Options
In terms of material options, 3D printing offers good material options to choose from. Although some materials may require different 3D printer models. This is because certain materials don’t work well with just one type of 3D printer. Whereas with traditional manufacturing, you can work with a variety of material options with just injection molding.
Time and Cost
Time and cost are always crucial for any business. When time and cost are properly utilized, it lessens the time for labor and production, producing more products in less time, which avoids any tendencies for wasted time and money that won’t be profitable for the business.
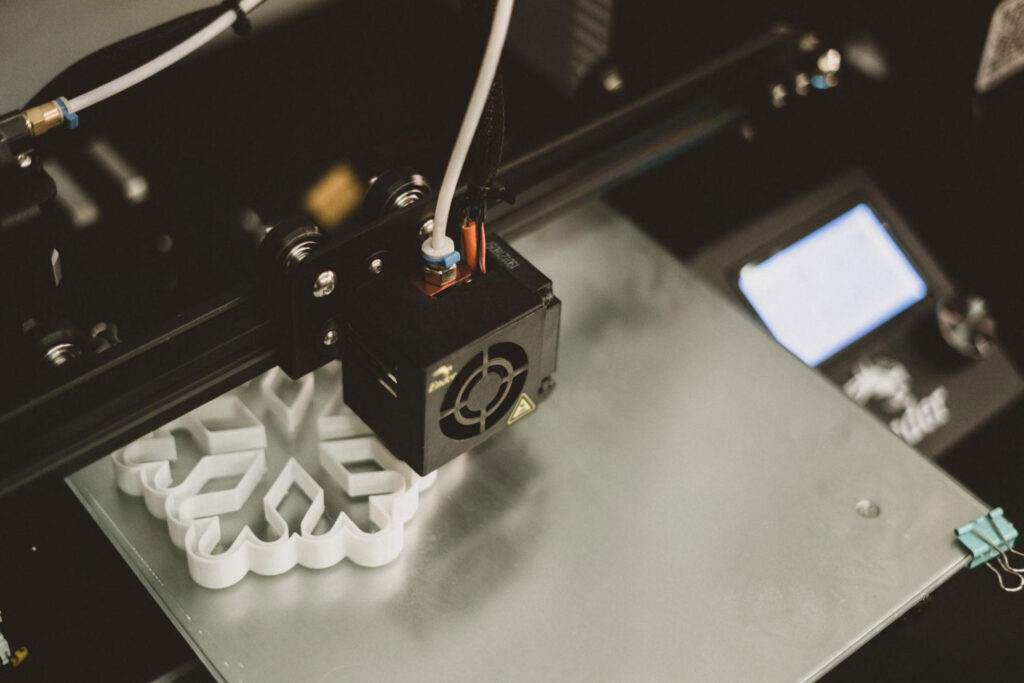
Since a traditional manufacturing process would require molding, producing parts would usually take a longer time, and can take months to create. This makes a huge impact not only on the time, but also on the costs because you’ll only be spending money on a single product mold. Another downside to this is that you may have to wait a bit more just to get the part. On the other hand, with 3D printing, the use of molds is not required because this process deposits material layer by layer in the printing bed. Unlike traditional manufacturing, 3D printing or additive manufacturing doesn’t take a long time to produce a part and its lead time may only take a few days, making it both time and cost-effective.
Quantity of Production
Despite the ability to produce parts at faster speeds, it can still be difficult for 3D printing to produce parts at a large-scale. Since the additive manufacturing process involves creating parts layer by layer with each layer placed directly on top of the previous one, it can take hours to make the part itself. While with traditional manufacturing, production of dozens or even hundreds of similar products is possible. This means that injection molding plastic parts and assembling can be done in just a certain amount of time.
Looking for quality 3D printing in the Philippines? Contact us today to know more about our products!














